
1. What is an Information Security Assurance?

Information assurance and security is the management and protection of knowledge, information, and data. It combines two fields: Information assurance, which focuses on ensuring the availability, integrity, authentication, confidentiality, and non-repudiation of information and systems. Information security, which centers on the protection of information and information systems from unauthorized access, use, disclosure, disruption, modification, or destruction in order to provide confidentiality, integrity, and availability.
2. Components Information Security Assurance?
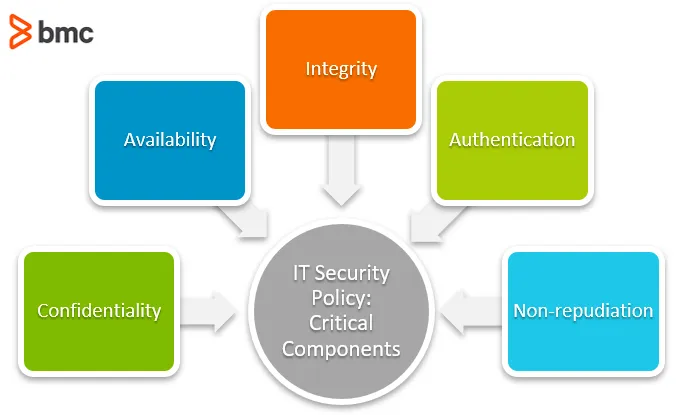
The components Information Security Assurance are confidentiality, integrity, availability, authenticity, and non-repudiation.
Confidentiality refers to the concealment. It means that the information is visible to the authorized eyes only. Keeping the information from unauthorized viewers is the first step to the information security. This component gains importance especially in fields that deal with sensitive information like social security numbers, addresses and such.
Integrity means the ‘originality’ of the information. This component aims to make sure that the information is intact and unaltered. As a result, assuring that the information is not altered by mistake, malicious action or even a natural disaster falls within the scope of integrity.
Availability of the information is a pretty straightforward concept. It refers to having access to the information when needed. Availability gains additional importance because of the malicious attacks that aim to hinder authorized users from accessing the data.
Authenticity refers to the state of being genuine, verifiable or trustable. Accountability on the other hand, refers to the ability to trace back the actions to the entity that is responsible for them. It is especially important for fault isolation, detection, nonrepudiation and deterrence.
3. Differentiate the certification programs to Common body language?

Body language is a form of non-verbal communication that encompasses both conscious and unconscious gestures that we make. A person is considered a good communicator when s/he is attentive and skilled in recognizing such gestures. Body language is an intricate subject and detailed insights described in the course reveal the secrets of successful communication.
4. Differentiate the Governance and Risk management?
Governance, or corporate governance, is the overall system of rules, practices, and standards that guide a business. Risk, or enterprise risk management, is the process of identifying potential hazards to the business and acting to reduce or eliminate their financial impact.
5. Different between Security Architecture to Design?
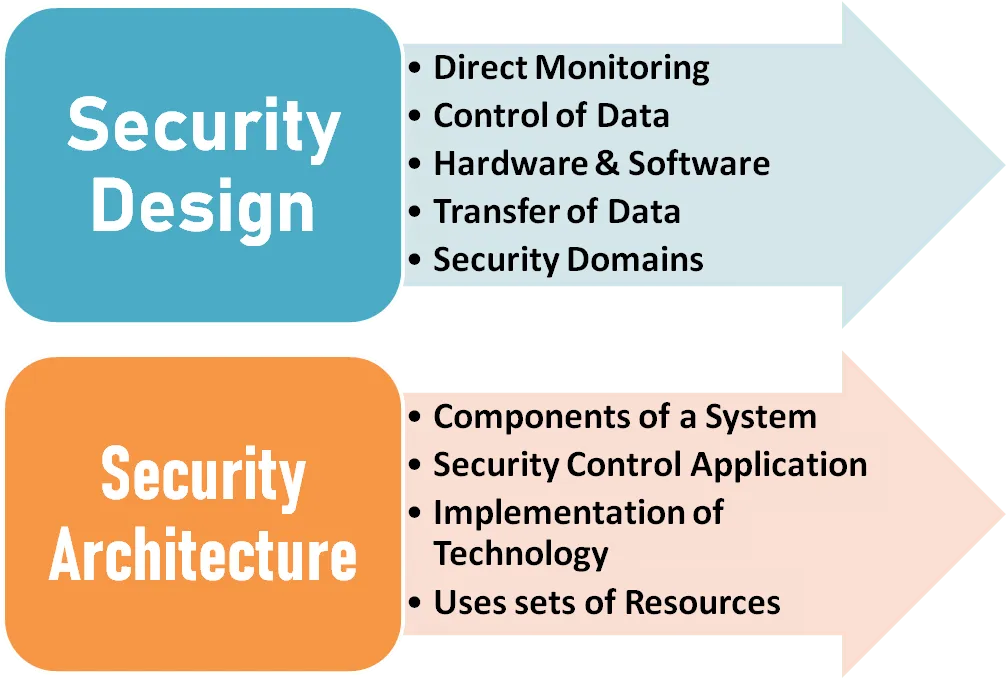
Security architecture is the set of resources and components of a security system that allow it to function. Security design refers to the techniques and methods that position those hardware and software elements to facilitate security.
6. Different between Business Continuity Planning to D-i-s-a-s-t-e-r Recovery Planning?
Business continuity focuses on keeping business operational during a disaster to disaster recovery focuses on restoring data access and IT infrastructure after a disaster. So that, the disaster recovery helps to ensure an organization's ability to return to full functionality after a disaster occurs.
7. What is Physical Security Control?

Physical security controls, to include deterrent, detective, and preventive measures, are the means we put in place to mitigate physical security issues. Protecting people is the foremost concern when planning our physical security.
8. What is Operations Security?
Operations Security is the process by which we protect critical information whether it is classified or unclassified that can be used against us. It focuses on preventing our adversaries' access to information and actions that may compromise an operation.
9. What is Law?

Law are rules adopted and enforced by governments to codify in modern society. The law of network society regulates information security generally and in its particular fields.
10. What is Investigation?
A security investigation established what caused the incident and how far it compromised or threatened the security of people, information, or assets.
11. What is Ethics?
Ethics can be defined as a moral code by which personal lives. In computer security, cyber-ethics is what separates security personnel from the hackers. It’s the knowledge of right and wrong, and the ability to adhere to ethical principles while on the job.
12. What is Information Security?

Information security is a set of practices designed to keep personal data secure from unauthorized access and alteration during storing or transmitting from one pace to another.
